Pitch Recipes¶
Babbitt Example¶
Derived tone rows from inversionally related interval cycles in Milton Babbitt’s Partitions for Piano:
Define helper function for creating interval cycles:
>>> import abjad
>>> def perle_cyclic_set(starting_pitch, interval):
... returned_list = [starting_pitch]
... for _ in range(10):
... val = returned_list[-1] + interval
... val %= 12
... returned_list.append(val)
... return returned_list
...
Define helper function to intersect cycles:
>>> def intersect_sequences(seq_1, seq_2, pattern_1, pattern_2, length):
... returned_list = []
... for index in range(length):
... match_1 = pattern_1.matches_index(index, length)
... match_2 = pattern_2.matches_index(index, length)
... if match_1:
... value = seq_1.pop(0)
... returned_list.append(value)
... elif match_2:
... value = seq_2.pop(0)
... returned_list.append(value)
... else:
... returned_list.append(None)
... return returned_list
...
Create first intersection:
>>> ic1_p5 = perle_cyclic_set(starting_pitch=5, interval=1)
>>> ic1_p2 = perle_cyclic_set(starting_pitch=2, interval=1)
>>> ic1_p5_pattern = abjad.Pattern(
... indices=[0, 2, 4],
... period=6,
... )
>>> ic1_p2_pattern = abjad.Pattern(
... indices=[1, 3, 5],
... period=6,
... )
>>> intersection_1 = intersect_sequences(
... ic1_p5, ic1_p2, ic1_p5_pattern, ic1_p2_pattern, 6
... )
Create second intersection:
>>> ic11_p10 = perle_cyclic_set(starting_pitch=10, interval=11)
>>> ic11_p1 = perle_cyclic_set(starting_pitch=1, interval=11)
>>> ic11_p10_pattern = abjad.Pattern(
... indices=[0, 2, 4],
... period=6,
... )
>>> ic11_p1_pattern = abjad.Pattern(
... indices=[1, 3, 5],
... period=6,
... )
>>> intersection_2 = intersect_sequences(
... ic11_p10, ic11_p1, ic11_p10_pattern, ic11_p1_pattern, 6
... )
Create and override staff:
>>> row = abjad.TwelveToneRow(intersection_1 + intersection_2)
>>> staff = abjad.Staff([abjad.Note(_, (1, 8)) for _ in row])
>>> abjad.attach(abjad.TimeSignature((6, 8)), staff[0])
>>> abjad.Label(staff).with_intervals(prototype=abjad.NumberedIntervalClass)
>>> abjad.override(staff).Beam.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(staff).Flag.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(staff).Stem.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(staff).text_script.staff_padding = 4
>>> abjad.override(staff).TimeSignature.stencil = "##f"
>>> score = abjad.Score([staff])
>>> abjad.setting(score).proportional_notation_duration = "#(ly:make-moment 1 20)"
Show score:
>>> abjad.show(score)
Carter Example¶
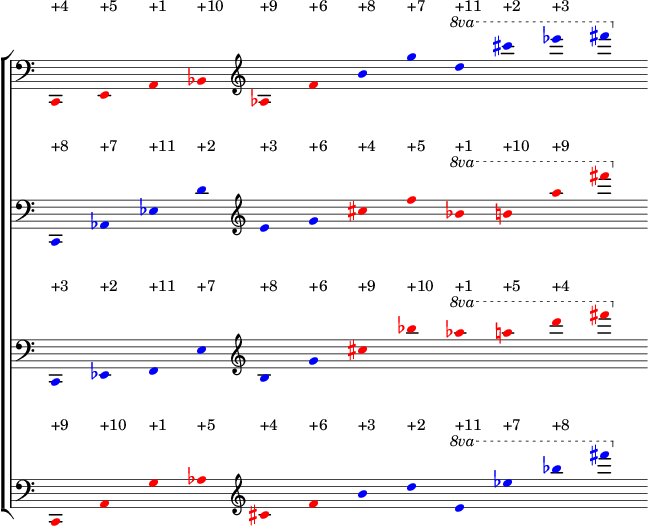
Elliott Carter’s parallel-inverted all-interval collections:
Define appropriately invertible hexachords:
>>> import abjad
>>> score = abjad.Score()
>>> group = abjad.StaffGroup()
>>> source_hex = abjad.PitchClassSegment([0, 4, 9, 10, 8, 5])
>>> source_hexachords = [
... source_hex,
... source_hex.invert(),
... source_hex.retrograde().transpose((0 - source_hex[-1].number)),
... source_hex.retrograde().transpose((0 - source_hex[-1].number)).invert(),
... ]
Iterate over hexachords, combining with hexachord inversion transposed six semitones above the final hexachord pitch, stacking each pitch as an interval above the previous pitch:
>>> for hexachord in source_hexachords:
... s1 = hexachord
... s2 = s1.invert().transpose(s1[-1].number + 6)
... full_sequence = abjad.PitchSegment(s1 + s2)
... transposed_sequence = full_sequence.transpose(-24)
... vertical_sequence = [-24]
... for pitch in transposed_sequence[1:]:
... pitch_number = pitch.number
... while pitch_number < vertical_sequence[-1]:
... pitch_number += 12
... vertical_sequence.append(pitch_number)
... staff = abjad.Staff([abjad.Note(_, (1, 16)) for _ in vertical_sequence])
... abjad.attach(abjad.Clef("bass"), staff[0])
... abjad.attach(abjad.Clef("treble"), staff[4])
... abjad.ottava(staff[8:])
... abjad.Label(staff).with_intervals(prototype=abjad.NumberedIntervalClass)
... abjad.override(staff).text_script.staff_padding = 7
... group.append(staff)
...
Add staff group to score and override settings:
>>> score.append(group)
>>> abjad.override(score).Beam.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(score).Flag.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(score).Stem.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(score).TimeSignature.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(
... score
... ).StaffGrouper.staff_staff_spacing = (
... "#'((basic-distance . 20) (minimum-distance . 20) (padding . 2))"
... )
>>> abjad.setting(score).proportional_notation_duration = "#(ly:make-moment 1 45)"
>>> abjad.Label(group[0][:6]).color_leaves("#red")
>>> abjad.Label(group[0][6:]).color_leaves("#blue")
>>> abjad.Label(group[1][:6]).color_leaves("#blue")
>>> abjad.Label(group[1][6:]).color_leaves("#red")
>>> abjad.Label(group[2][:6]).color_leaves("#blue")
>>> abjad.Label(group[2][6:]).color_leaves("#red")
>>> abjad.Label(group[3][:6]).color_leaves("#red")
>>> abjad.Label(group[3][6:]).color_leaves("#blue")
>>> score_block = abjad.Block(name="score")
>>> score_block.items.append(score)
>>> file = abjad.LilyPondFile(
... items=[score_block],
... includes=["abjad.ily"],
... )
Show file:
>>> abjad.show(file)
Hoffman Example¶
Non-octave-iterating scale in Joel Hoffman’s Piano Concerto:
Define source scale and interval of replication:
>>> import abjad
>>> interval_down = abjad.NamedInterval("-M9")
>>> cell = abjad.PitchSegment(
... [
... "bf''''",
... "af''''",
... "g''''",
... "fs''''",
... "f''''",
... "ef''''",
... "d''''",
... "cs''''",
... "c''''",
... "b'''",
... "a'''",
... ]
... )
Collect transpositions of scales:
>>> cells = [cell]
>>> for _ in range(5):
... new_cell = cells[-1].transpose(interval_down)
... cells.append(new_cell)
...
>>> full_scale = []
>>> for cell in cells:
... full_scale.extend(cell)
...
>>> full_scale.sort()
>>> final_set = abjad.PitchSegment([_ for _ in full_scale])
Create notes from pitch segment:
>>> staff = abjad.Staff(
... [abjad.Note(abjad.NumberedPitch(_), (1, 16)) for _ in final_set]
... )
Attach extra attachments and override score settings:
>>> abjad.attach(abjad.Clef("bass"), staff[0])
>>> for note in abjad.select(staff).leaves():
... if note.written_pitch == "c'":
... abjad.attach(abjad.Clef("treble"), note)
...
>>> abjad.ottava(staff[:11], start_ottava=abjad.Ottava(n=-1))
>>> abjad.ottava(staff[44:])
>>> abjad.override(staff).BarLine.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(staff).Beam.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(staff).Flag.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(staff).Stem.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(staff).TimeSignature.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.setting(staff).proportional_notation_duration = "#(ly:make-moment 1 25)"
>>> colors = [
... "#red",
... "#blue",
... "#red",
... "#blue",
... "#red",
... "#blue",
... ]
>>> leaf_group = (
... abjad.select(staff)
... .leaves()
... .partition_by_counts(
... [11],
... cyclic=True,
... overhang=True,
... )
... )
>>> for color, leaves in zip(colors, leaf_group):
... abjad.Label(leaves).color_leaves(color)
...
>>> score_block = abjad.Block(name="score")
>>> score_block.items.append(staff)
>>> paper_block = abjad.Block(name="paper")
>>> paper_block.items.append("indent = 0")
>>> file = abjad.LilyPondFile(
... items=[paper_block, score_block], includes=["abjad.ily"]
... )
Show file:
>>> abjad.show(file)
Nono Example¶
Double-stop creation from hexachord pairs in Luigi Nono’s Fragmente – Stille, an Diotima:
Define tone row and divide into hexachords:
>>> scale = abjad.PitchSegment(
... [
... "cs''",
... "d''",
... "ef''",
... "e''",
... "f''",
... "fs''",
... "g''",
... "gs''",
... "a''",
... "bf''",
... "b''",
... "c'''",
... ]
... )
>>> hexachord_1 = [_ for _ in scale[:6]]
>>> hexachord_2 = [_ for _ in scale[6:]]
Isolate diads from paired hexachords:
>>> diads = [list(_) for _ in zip(hexachord_1, hexachord_2)]
>>> reversed_indices = [1, 2, 4, 5]
>>> for index in reversed_indices:
... diads[index] = (diads[index][1], diads[index][0])
...
>>> staff = abjad.Staff()
>>> for diad in diads:
... lower = diad[0]
... higher = diad[1]
... while higher < lower:
... higher = abjad.NamedInterval("+P8").transpose(higher)
... chord = abjad.Chord([lower, higher], (1, 8))
... staff.append(chord)
...
Change octaves:
>>> staff[2].written_pitches = abjad.NamedInterval("+P8").transpose(
... staff[2].written_pitches
... )
>>> staff[3].written_pitches = abjad.NamedInterval("+P8").transpose(
... staff[3].written_pitches
... )
>>> staff[4].written_pitches = abjad.NamedInterval("-P8").transpose(
... staff[4].written_pitches
... )
>>> staff[5].written_pitches = abjad.NumberedInterval("-24").transpose(
... staff[5].written_pitches
... )
Override staff settings:
>>> abjad.override(staff).Beam.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(staff).Flag.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(staff).Stem.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(staff).text_script.staff_padding = 4
>>> abjad.override(staff).TimeSignature.stencil = "##f"
>>> score = abjad.Score([staff])
>>> abjad.setting(score).proportional_notation_duration = "#(ly:make-moment 1 20)"
Show score:
>>> abjad.show(score)
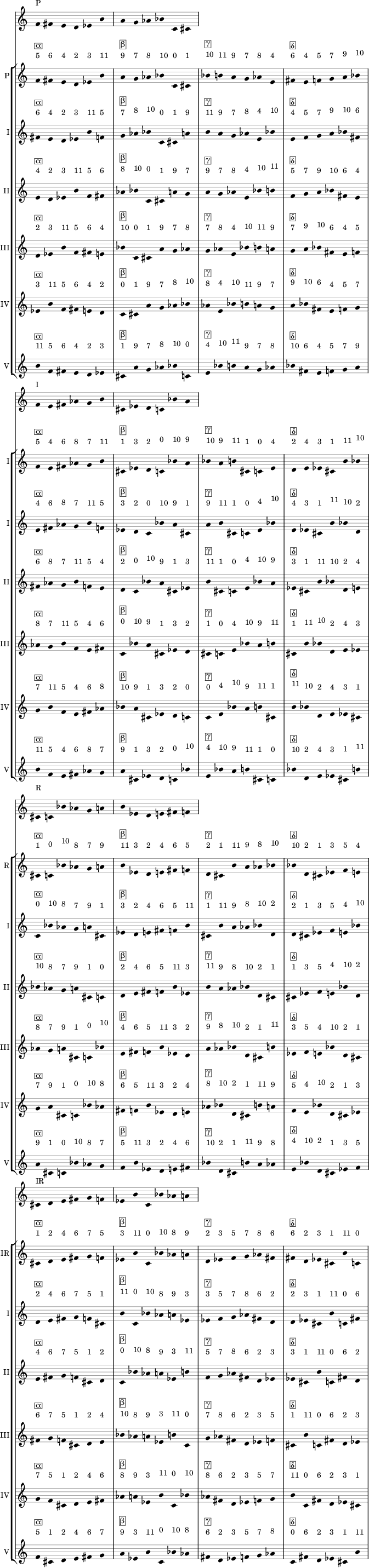
Stravinsky Example¶
Tone row rotation in Igor Stravinsky’s Abraham and Isaac:
Define tone row and row permutations:
>>> import abjad
>>> file = abjad.LilyPondFile()
>>> source = abjad.TwelveToneRow([5, 6, 4, 2, 3, 11, 9, 7, 8, 10, 0, 1])
>>> perms = [
... source,
... source.invert(),
... source.retrograde(),
... abjad.TwelveToneRow(source.retrograde()).invert(),
... ]
>>> labels = [
... abjad.Markup(
... r"\markup P",
... literal=True,
... direction=abjad.Up,
... ),
... abjad.Markup(
... r"\markup I",
... literal=True,
... direction=abjad.Up,
... ),
... abjad.Markup(
... r"\markup R",
... literal=True,
... direction=abjad.Up,
... ),
... abjad.Markup(
... r"\markup IR",
... literal=True,
... direction=abjad.Up,
... ),
... ]
Define rotation distances and iterate through permutations, creating charts:
>>> rotations = [0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5]
>>> for perm, label in zip(perms, labels):
... source_staff = abjad.Staff([abjad.Note(_, (1, 16)) for _ in perm])
... abjad.attach(label, source_staff[0])
... score = abjad.Score([source_staff])
... group = abjad.StaffGroup()
... hexachords = [
... [_.number for _ in perm[:6]],
... [_.number for _ in perm[6:]],
... ]
... margin_markups = [
... abjad.StartMarkup(markup=label),
... abjad.StartMarkup(markup="I"),
... abjad.StartMarkup(markup="II"),
... abjad.StartMarkup(markup="III"),
... abjad.StartMarkup(markup="IV"),
... abjad.StartMarkup(markup="V"),
... ]
... for r, m in zip(rotations, margin_markups):
... staff = abjad.Staff()
... sets = [
... abjad.PitchClassSegment(hexachords[0]).rotate(r),
... abjad.PitchClassSegment(hexachords[1]).rotate(r),
... abjad.PitchClassSegment(hexachords[0])
... .rotate(r) # transpose to zero since stravinsky keyword is removed
... .transpose(hexachords[0][0]),
... abjad.PitchClassSegment(hexachords[1])
... .rotate(r) # transpose to zero since stravinsky keyword is removed
... .transpose(hexachords[1][0]),
... ]
... names = [
... abjad.Markup(r"\markup \box α", literal=True, direction=abjad.Up),
... abjad.Markup(r"\markup \box β", literal=True, direction=abjad.Up),
... abjad.Markup(r"\markup \box γ", literal=True, direction=abjad.Up),
... abjad.Markup(r"\markup \box δ", literal=True, direction=abjad.Up),
... ]
... for set, name in zip(sets, names):
... voice = abjad.Voice([abjad.Note(_, (1, 16)) for _ in set])
... for leaf in abjad.iterate(voice).leaves():
... mark = abjad.Markup(
... f"\markup {abjad.NumberedPitchClass(leaf.written_pitch)}",
... literal=True,
... direction=abjad.Up,
... )
... abjad.tweak(mark).staff_padding = "3"
... abjad.attach(mark, leaf)
... abjad.tweak(name).staff_padding = "3"
... abjad.attach(name, voice[0])
... abjad.attach(abjad.TimeSignature((6, 16)), voice[0])
... staff.append(voice)
... abjad.attach(m, abjad.select(staff).leaf(0))
... group.append(staff)
... score.append(group)
... abjad.override(score).Beam.stencil = "##f"
... abjad.override(score).Flag.stencil = "##f"
... abjad.override(score).Stem.stencil = "##f"
... abjad.override(score).TimeSignature.stencil = "##f"
... abjad.override(
... score
... ).StaffGrouper.staff_staff_spacing = (
... "#'((basic-distance . 10) (minimum-distance . 10) (padding . 2))"
... )
... abjad.setting(
... score
... ).proportional_notation_duration = r"#(ly:make-moment 1 25)"
... file.items.append(score)
...
Show file of chart scores:
>>> abjad.show(file)
Xenakis Example¶
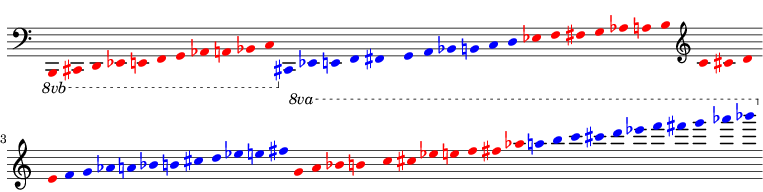
Pitch sieve in Iannis Xenakis’s Jonchaies:
Initialize periodic patterns and create union:
>>> import abjad
>>> x17_0 = abjad.Pattern(indices=[0], period=17)
>>> x17_1 = abjad.Pattern(indices=[1], period=17)
>>> x17_4 = abjad.Pattern(indices=[4], period=17)
>>> x17_5 = abjad.Pattern(indices=[5], period=17)
>>> x17_7 = abjad.Pattern(indices=[7], period=17)
>>> x17_11 = abjad.Pattern(indices=[11], period=17)
>>> x17_12 = abjad.Pattern(indices=[12], period=17)
>>> x17_16 = abjad.Pattern(indices=[16], period=17)
>>> sieve = x17_0 | x17_1 | x17_4 | x17_5 | x17_7 | x17_11 | x17_12 | x17_16
Iterate through boolean vector to create pitch list:
>>> pitches = []
>>> length = 56
>>> indices = [_ for _ in range(length)]
>>> vector = sieve.get_boolean_vector(total_length=length)
>>> for index, boolean_value in zip(indices, vector):
... if boolean_value:
... pitches.append(abjad.NumberedPitch(index))
...
Initialize note objects from pitch list:
>>> staff = abjad.Staff([abjad.Note(_ - 15, (1, 16)) for _ in pitches])
>>> abjad.attach(abjad.Clef("bass"), staff[0])
>>> abjad.attach(abjad.Clef("treble"), staff[7])
>>> abjad.ottava(staff[21:])
>>> abjad.override(staff).BarLine.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(staff).Beam.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(staff).Flag.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(staff).Stem.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.override(staff).TimeSignature.stencil = "##f"
>>> abjad.setting(staff).proportional_notation_duration = r"#(ly:make-moment 1 25)"
Show score:
>>> abjad.show(staff)